本项目基于:
Ubuntu2204
Eigen3
因为电赛备赛需要,所以抽空研究了一下卡尔曼滤波。
文件目录如下:
.
├── CMakeLists.txt
├── CMakePresets.jso
├── config
│ └── kalman_config.yaml
├── include
│ ├── ballsensor.hpp
│ └── kalman.hpp
└── src
├── ballsensor.cpp
├── kalman.cpp
├── kalman_filter_results.png
├── main.cpp
└── show.py首先,因为我这边还没有场地所以模拟了一个ballsensor.cpp 作为输入xy,还会随机输入噪声
#ifndef BALL_SENSOR_H
#define BALL_SENSOR_H
#include <vector>
#include <random>
#include <Eigen/Dense>
#include <string>
class BallSensor {
private:
// 真实状态变量
double true_x, true_y; // 位置
double true_vx, true_vy; // 速度
double true_ax, true_ay; // 加速度
// 随机数生成器
std::default_random_engine generator;
std::normal_distribution<double> noise_distribution;
// 测量噪声标准差
double measurement_noise_std;
// 时间步长
double dt;
// 存储轨迹和测量值
std::vector<Eigen::Vector2d> true_positions;
std::vector<Eigen::Vector2d> measurements;
// 当前时间
double current_time;
public:
// 构造函数
BallSensor(double noise_std = 0.1, double time_step = 0.1);
// 从配置文件初始化
void initFromConfig(const std::string& config_file);
// 初始化球的状态
void initialize(double x0, double y0, double vx0, double vy0, double ax0, double ay0);
// 更新球的真实位置
void updateTrueState();
// 获取带有噪声的测量值
Eigen::Vector2d getMeasurement();
// 获取当前时间
double getCurrentTime() const { return current_time; }
// 获取真实状态
Eigen::Vector2d getTruePosition() const;
Eigen::Vector2d getTrueVelocity() const;
Eigen::Vector2d getTrueAcceleration() const;
// 获取历史数据
const std::vector<Eigen::Vector2d>& getTruePositions() const { return true_positions; }
const std::vector<Eigen::Vector2d>& getMeasurements() const { return measurements; }
};
#endif // BALL_SENSOR_H#include "../include/ballsensor.hpp"
#include <yaml-cpp/yaml.h>
#include <chrono>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
BallSensor::BallSensor(double noise_std, double time_step)
: measurement_noise_std(noise_std), dt(time_step), current_time(0.0) {
// 初始化随机数生成器
unsigned seed = std::chrono::system_clock::now().time_since_epoch().count();
generator = std::default_random_engine(seed);
// 配置高斯分布噪声
noise_distribution = std::normal_distribution<double>(0.0, measurement_noise_std);
}
void BallSensor::initialize(double x0, double y0, double vx0, double vy0, double ax0, double ay0) {
true_x = x0;
true_y = y0;
true_vx = vx0;
true_vy = vy0;
true_ax = ax0;
true_ay = ay0;
current_time = 0.0;
// 清除历史数据
true_positions.clear();
measurements.clear();
// 记录初始位置
Eigen::Vector2d initial_position(true_x, true_y);
true_positions.push_back(initial_position);
// 记录初始带噪声测量值
measurements.push_back(getMeasurement());
}
void BallSensor::updateTrueState() {
// 运动学方程:更新位置和速度
true_x += true_vx * dt + 0.5 * true_ax * dt * dt;
true_y += true_vy * dt + 0.5 * true_ay * dt * dt;
true_vx += true_ax * dt;
true_vy += true_ay * dt;
// 小概率随机改变加速度,模拟不平整的倾斜平面
std::uniform_real_distribution<double> random_change(0.0, 1.0);
if (random_change(generator) < 0.05) { // 5%的概率改变加速度
std::normal_distribution<double> acc_change(0.0, 0.05);
true_ax += acc_change(generator);
true_ay += acc_change(generator);
// 限制加速度范围,防止过大
if (std::abs(true_ax) > 0.5) true_ax *= 0.8;
if (std::abs(true_ay) > 0.5) true_ay *= 0.8;
}
// 增加时间
current_time += dt;
// 存储真实位置
true_positions.push_back(Eigen::Vector2d(true_x, true_y));
}
Eigen::Vector2d BallSensor::getMeasurement() {
// 生成带有噪声的测量值
double measured_x = true_x + noise_distribution(generator);
double measured_y = true_y + noise_distribution(generator);
Eigen::Vector2d measurement(measured_x, measured_y);
measurements.push_back(measurement);
return measurement;
}
Eigen::Vector2d BallSensor::getTruePosition() const {
return Eigen::Vector2d(true_x, true_y);
}
Eigen::Vector2d BallSensor::getTrueVelocity() const {
return Eigen::Vector2d(true_vx, true_vy);
}
Eigen::Vector2d BallSensor::getTrueAcceleration() const {
return Eigen::Vector2d(true_ax, true_ay);
}
void BallSensor::initFromConfig(const std::string& config_file) {
try {
// 加载YAML文件
YAML::Node config = YAML::LoadFile(config_file);
// 读取传感器设置
measurement_noise_std = config["sensor"]["measurement_noise_std"].as<double>();
dt = config["sensor"]["time_step"].as<double>();
// 重新配置噪声分布
noise_distribution = std::normal_distribution<double>(0.0, measurement_noise_std);
// 初始化随机数生成器
unsigned seed = std::chrono::system_clock::now().time_since_epoch().count();
generator = std::default_random_engine(seed);
// 初始化球的状态
double x0 = config["initial_state"]["x"].as<double>();
double y0 = config["initial_state"]["y"].as<double>();
double vx0 = config["initial_state"]["vx"].as<double>();
double vy0 = config["initial_state"]["vy"].as<double>();
double ax0 = config["initial_state"]["ax"].as<double>();
double ay0 = config["initial_state"]["ay"].as<double>();
// 初始化球的状态
initialize(x0, y0, vx0, vy0, ax0, ay0);
std::cout << "传感器模拟器已从配置文件成功初始化: " << config_file << std::endl;
} catch (const YAML::Exception& e) {
std::cerr << "读取配置文件时出错: " << e.what() << std::endl;
throw;
} catch (const std::exception& e) {
std::cerr << "初始化传感器模拟器时出错: " << e.what() << std::endl;
throw;
}
}关键的卡尔曼滤波器在这里:
因为调参的时候可能经常要改参数,我就把它写成个个yaml,方便我随时改参而不用重新build
# 卡尔曼滤波器配置文件
# 基本设置
time_step: 0.1 # 时间步长 (秒)
# 状态初始化
initial_state:
x: 0.0 # 初始x位置
y: 0.0 # 初始y位置
vx: 1.0 # 初始x方向速度 (每秒1个单位)
vy: 1.5 # 初始y方向速度 (每秒1.5个单位)
ax: 0.2 # 初始x方向加速度 (每秒每秒0.2个单位)
ay: -0.1 # 初始y方向加速度 (每秒每秒-0.1个单位,负值表示减速)
# 初始协方差矩阵对角元素
initial_covariance:
x: 0.1 # x位置的初始不确定性
y: 0.1 # y位置的初始不确定性
vx: 1.0 # x方向速度的初始不确定性
vy: 1.0 # y方向速度的初始不确定性
ax: 2.0 # x方向加速度的初始不确定性
ay: 2.0 # y方向加速度的初始不确定性
# 噪声设置
noise:
process:
default: 0.01 # 默认过程噪声
position:
x: 0.01 # x位置的过程噪声
y: 0.01 # y位置的过程噪声
velocity:
x: 0.01 # x速度的过程噪声
y: 0.01 # y速度的过程噪声
acceleration:
x: 0.1 # x加速度的过程噪声
y: 0.1 # y加速度的过程噪声
measurement:
position:
x: 0.1 # x位置的测量噪声
y: 0.1 # y位置的测量噪声
# 传感器模拟器设置
sensor:
measurement_noise_std: 0.1 # 传感器噪声标准差
time_step: 0.1 # 传感器采样时间步长
我把他写成了一个类
#ifndef KALMAN_FILTER_H
#define KALMAN_FILTER_H
#include <Eigen/Dense>
#include <string>
class KalmanFilter {
private:
// 状态向量: [x, y, vx, vy, ax, ay]^T
Eigen::VectorXd x;
// 状态协方差矩阵
Eigen::MatrixXd P;
// 状态转移矩阵
Eigen::MatrixXd F;
// 测量矩阵
Eigen::MatrixXd H;
// 过程噪声协方差
Eigen::MatrixXd Q;
// 测量噪声协方差
Eigen::MatrixXd R;
// 时间步长
double dt;
public:
// 构造函数
KalmanFilter();
// 从配置文件初始化滤波器
void initFromConfig(const std::string& config_file);
// 手动初始化滤波器
void init(double dt, const Eigen::VectorXd& initial_state, const Eigen::MatrixXd& initial_covariance);
// 预测步骤
void predict();
// 更新步骤
void update(const Eigen::VectorXd& measurement);
// 获取当前状态
const Eigen::VectorXd& getState() const { return x; }
// 获取当前协方差
const Eigen::MatrixXd& getCovariance() const { return P; }
};
#endif // KALMAN_FILTER_H#include "../include/kalman.hpp"
#include <yaml-cpp/yaml.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
KalmanFilter::KalmanFilter() {
// 默认构造函数
}
void KalmanFilter::initFromConfig(const std::string& config_file) {
try {
// 加载YAML文件
YAML::Node config = YAML::LoadFile(config_file);
// 读取时间步长
dt = config["time_step"].as<double>();
// 设置状态维度为6:[x, y, vx, vy, ax, ay]
int state_dim = 6;
// 设置测量维度为2:[x, y]
int meas_dim = 2;
// 初始化状态向量
x = Eigen::VectorXd(state_dim);
x(0) = config["initial_state"]["x"].as<double>();
x(1) = config["initial_state"]["y"].as<double>();
x(2) = config["initial_state"]["vx"].as<double>();
x(3) = config["initial_state"]["vy"].as<double>();
x(4) = config["initial_state"]["ax"].as<double>();
x(5) = config["initial_state"]["ay"].as<double>();
// 初始化状态协方差矩阵
P = Eigen::MatrixXd::Zero(state_dim, state_dim);
P(0, 0) = config["initial_covariance"]["x"].as<double>();
P(1, 1) = config["initial_covariance"]["y"].as<double>();
P(2, 2) = config["initial_covariance"]["vx"].as<double>();
P(3, 3) = config["initial_covariance"]["vy"].as<double>();
P(4, 4) = config["initial_covariance"]["ax"].as<double>();
P(5, 5) = config["initial_covariance"]["ay"].as<double>();
// 构建状态转移矩阵 F
F = Eigen::MatrixXd::Identity(state_dim, state_dim);
F(0, 2) = dt; // x与vx的关系
F(0, 4) = 0.5*dt*dt; // x与ax的关系
F(1, 3) = dt; // y与vy的关系
F(1, 5) = 0.5*dt*dt; // y与ay的关系
F(2, 4) = dt; // vx与ax的关系
F(3, 5) = dt; // vy与ay的关系
// 构建测量矩阵 H
H = Eigen::MatrixXd::Zero(meas_dim, state_dim);
H(0, 0) = 1.0; // 测量x
H(1, 1) = 1.0; // 测量y
// 设置过程噪声协方差矩阵 Q
double process_noise = config["noise"]["process"]["default"].as<double>();
Q = Eigen::MatrixXd::Identity(state_dim, state_dim) * process_noise;
// 设置特定状态变量的过程噪声
Q(0, 0) = config["noise"]["process"]["position"]["x"].as<double>();
Q(1, 1) = config["noise"]["process"]["position"]["y"].as<double>();
Q(2, 2) = config["noise"]["process"]["velocity"]["x"].as<double>();
Q(3, 3) = config["noise"]["process"]["velocity"]["y"].as<double>();
Q(4, 4) = config["noise"]["process"]["acceleration"]["x"].as<double>();
Q(5, 5) = config["noise"]["process"]["acceleration"]["y"].as<double>();
// 设置测量噪声协方差矩阵 R
R = Eigen::MatrixXd::Zero(meas_dim, meas_dim);
R(0, 0) = config["noise"]["measurement"]["position"]["x"].as<double>();
R(1, 1) = config["noise"]["measurement"]["position"]["y"].as<double>();
std::cout << "卡尔曼滤波器已从配置文件成功初始化: " << config_file << std::endl;
} catch (const YAML::Exception& e) {
std::cerr << "读取配置文件时出错: " << e.what() << std::endl;
throw;
} catch (const std::exception& e) {
std::cerr << "初始化卡尔曼滤波器时出错: " << e.what() << std::endl;
throw;
}
}
void KalmanFilter::init(double time_step, const Eigen::VectorXd& initial_state, const Eigen::MatrixXd& initial_covariance) {
dt = time_step;
// 设置状态维度为6:[x, y, vx, vy, ax, ay]
int state_dim = 6;
// 设置测量维度为2:[x, y]
int meas_dim = 2;
// 初始化状态向量
x = initial_state;
// 初始化状态协方差矩阵
P = initial_covariance;
// 构建状态转移矩阵 F
// 运动方程:
// x(t+dt) = x(t) + vx(t)*dt + 0.5*ax(t)*dt^2
// y(t+dt) = y(t) + vy(t)*dt + 0.5*ay(t)*dt^2
// vx(t+dt) = vx(t) + ax(t)*dt
// vy(t+dt) = vy(t) + ay(t)*dt
// ax(t+dt) = ax(t) (假设加速度保持不变)
// ay(t+dt) = ay(t) (假设加速度保持不变)
F = Eigen::MatrixXd::Identity(state_dim, state_dim);
F(0, 2) = dt; // x与vx的关系
F(0, 4) = 0.5*dt*dt; // x与ax的关系
F(1, 3) = dt; // y与vy的关系
F(1, 5) = 0.5*dt*dt; // y与ay的关系
F(2, 4) = dt; // vx与ax的关系
F(3, 5) = dt; // vy与ay的关系
// 构建测量矩阵 H
// 我们只测量位置 [x, y]
H = Eigen::MatrixXd::Zero(meas_dim, state_dim);
H(0, 0) = 1.0; // 测量x
H(1, 1) = 1.0; // 测量y
// 设置过程噪声协方差矩阵 Q
double process_noise = 0.01;
Q = Eigen::MatrixXd::Identity(state_dim, state_dim) * process_noise;
// 加速度的过程噪声可能更大,因为它代表了我们不确定的倾斜平面带来的加速度
Q(4, 4) = 0.1; // ax的过程噪声
Q(5, 5) = 0.1; // ay的过程噪声
// 设置测量噪声协方差矩阵 R
double measurement_noise = 0.1; // 传感器噪声
R = Eigen::MatrixXd::Identity(meas_dim, meas_dim) * measurement_noise;
}
void KalmanFilter::predict() {
// 预测步骤
// 预测状态: x = F * x
x = F * x;
// 预测协方差: P = F * P * F^T + Q
P = F * P * F.transpose() + Q;
}
void KalmanFilter::update(const Eigen::VectorXd& measurement) {
// 更新步骤
// 计算卡尔曼增益: K = P * H^T * (H * P * H^T + R)^-1
Eigen::MatrixXd PHt = P * H.transpose();
Eigen::MatrixXd S = H * PHt + R;
Eigen::MatrixXd K = PHt * S.inverse();
// 计算新的状态: x = x + K * (z - H * x)
// z是测量值,H * x是预测的测量值
Eigen::VectorXd y = measurement - H * x;
x = x + K * y;
// 更新状态协方差: P = (I - K * H) * P
int state_dim = x.size();
Eigen::MatrixXd I = Eigen::MatrixXd::Identity(state_dim, state_dim);
P = (I - K * H) * P;
}最终的main:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <iomanip> // 用于设置输出精度
#include "../include/ballsensor.hpp"
#include "../include/kalman.hpp"
int main() {
std::string config_file = "../config/kalman_config.yaml";
try {
// 创建传感器模拟器并从配置文件初始化
BallSensor sensor;
sensor.initFromConfig(config_file);
// 创建卡尔曼滤波器并从配置文件初始化
KalmanFilter kf;
kf.initFromConfig(config_file);
// 存储估计结果
std::vector<Eigen::Vector2d> estimated_positions;
std::vector<Eigen::Vector2d> estimated_velocities;
std::vector<Eigen::Vector2d> estimated_accelerations;
// 模拟100步
int num_steps = 500;
for (int i = 0; i < num_steps; ++i) {
// 更新传感器的真实状态
sensor.updateTrueState();
// 获取当前测量值
Eigen::Vector2d measurement = sensor.getMeasurement();
// 卡尔曼滤波预测步骤
kf.predict();
// 卡尔曼滤波更新步骤
kf.update(measurement);
// 获取滤波后的状态
Eigen::VectorXd state = kf.getState();
// 存储估计结果
estimated_positions.push_back(Eigen::Vector2d(state(0), state(1)));
estimated_velocities.push_back(Eigen::Vector2d(state(2), state(3)));
estimated_accelerations.push_back(Eigen::Vector2d(state(4), state(5)));
// 打印当前状态(每10步打印一次)
if (i % 10 == 0) {
std::cout << "步骤 " << i << ":" << std::endl;
std::cout << " 真实位置: ("
<< sensor.getTruePosition()[0] << ", "
<< sensor.getTruePosition()[1] << ")" << std::endl;
std::cout << " 测量位置: ("
<< measurement[0] << ", "
<< measurement[1] << ")" << std::endl;
std::cout << " 估计位置: ("
<< state(0) << ", "
<< state(1) << ")" << std::endl;
std::cout << " 估计速度: ("
<< state(2) << ", "
<< state(3) << ")" << std::endl;
std::cout << " 估计加速度: ("
<< state(4) << ", "
<< state(5) << ")" << std::endl;
std::cout << std::endl;
}
}
// 将结果保存到CSV文件中,用于后续可视化
std::ofstream result_file("kalman_filter_results.csv");
if (!result_file.is_open()) {
std::cerr << "无法创建结果文件" << std::endl;
return 1;
}
// 写入CSV文件头
result_file << "时间步,";
result_file << "真实位置X,真实位置Y,";
result_file << "测量位置X,测量位置Y,";
result_file << "估计位置X,估计位置Y,";
result_file << "真实速度X,真实速度Y,";
result_file << "估计速度X,估计速度Y,";
result_file << "真实加速度X,真实加速度Y,";
result_file << "估计加速度X,估计加速度Y" << std::endl;
// 写入所有数据
auto true_positions = sensor.getTruePositions();
auto measurements = sensor.getMeasurements();
for (int i = 0; i < num_steps; ++i) {
result_file << i << ",";
// 真实位置
result_file << true_positions[i][0] << "," << true_positions[i][1] << ",";
// 测量位置
result_file << measurements[i][0] << "," << measurements[i][1] << ",";
// 估计位置
result_file << estimated_positions[i][0] << "," << estimated_positions[i][1] << ",";
// 真实速度 (只有最后一步的)
if (i == num_steps - 1) {
Eigen::Vector2d true_vel = sensor.getTrueVelocity();
result_file << true_vel[0] << "," << true_vel[1] << ",";
} else {
// 可以通过位置差分来估计真实速度
double dt = sensor.getCurrentTime() / num_steps;
result_file << (true_positions[i+1][0] - true_positions[i][0]) / dt << ",";
result_file << (true_positions[i+1][1] - true_positions[i][1]) / dt << ",";
}
// 估计速度
result_file << estimated_velocities[i][0] << "," << estimated_velocities[i][1] << ",";
// 真实加速度 (最后一步的)
if (i == num_steps - 1) {
Eigen::Vector2d true_acc = sensor.getTrueAcceleration();
result_file << true_acc[0] << "," << true_acc[1] << ",";
} else if (i == num_steps - 2) {
// 最后第二步,简单差分
double dt = sensor.getCurrentTime() / num_steps;
result_file << "0,0,"; // 简化处理
} else {
// 可以通过速度差分来估计加速度
double dt = sensor.getCurrentTime() / num_steps;
double v1x = (true_positions[i+1][0] - true_positions[i][0]) / dt;
double v2x = (true_positions[i+2][0] - true_positions[i+1][0]) / dt;
double v1y = (true_positions[i+1][1] - true_positions[i][1]) / dt;
double v2y = (true_positions[i+2][1] - true_positions[i+1][1]) / dt;
result_file << (v2x - v1x) / dt << ",";
result_file << (v2y - v1y) / dt << ",";
}
// 估计加速度
result_file << estimated_accelerations[i][0] << "," << estimated_accelerations[i][1];
result_file << std::endl;
}
result_file.close();
std::cout << "模拟成功完成! 结果已保存到 kalman_filter_results.csv" << std::endl;
} catch (const std::exception& e) {
std::cerr << "错误: " << e.what() << std::endl;
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
CMakeLists.txt如下
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.10)
project(BallKalmanFilter)
# 设置C++标准
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 11)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD_REQUIRED ON)
# 查找Eigen库
find_package(Eigen3 REQUIRED)
include_directories(${EIGEN3_INCLUDE_DIR})
# 查找yaml-cpp库
find_package(yaml-cpp REQUIRED)
# 包含头文件目录
include_directories(include)
# 添加源文件
set(SOURCES
src/main.cpp
src/ballsensor.cpp
src/kalman.cpp
)
# 创建可执行文件
add_executable(ball_filter ${SOURCES})
# 链接库
target_link_libraries(ball_filter ${EIGEN3_LIBRARIES} yaml-cpp)
# 设置配置文件目录
file(COPY config DESTINATION ${CMAKE_BINARY_DIR})
最后写了个py来可视化图像
import zhplot
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib
import os
# 读取数据
df = pd.read_csv('build/kalman_filter_results.csv')
# 创建保存图形的目录
save_dir = 'build'
if not os.path.exists(save_dir):
os.makedirs(save_dir)
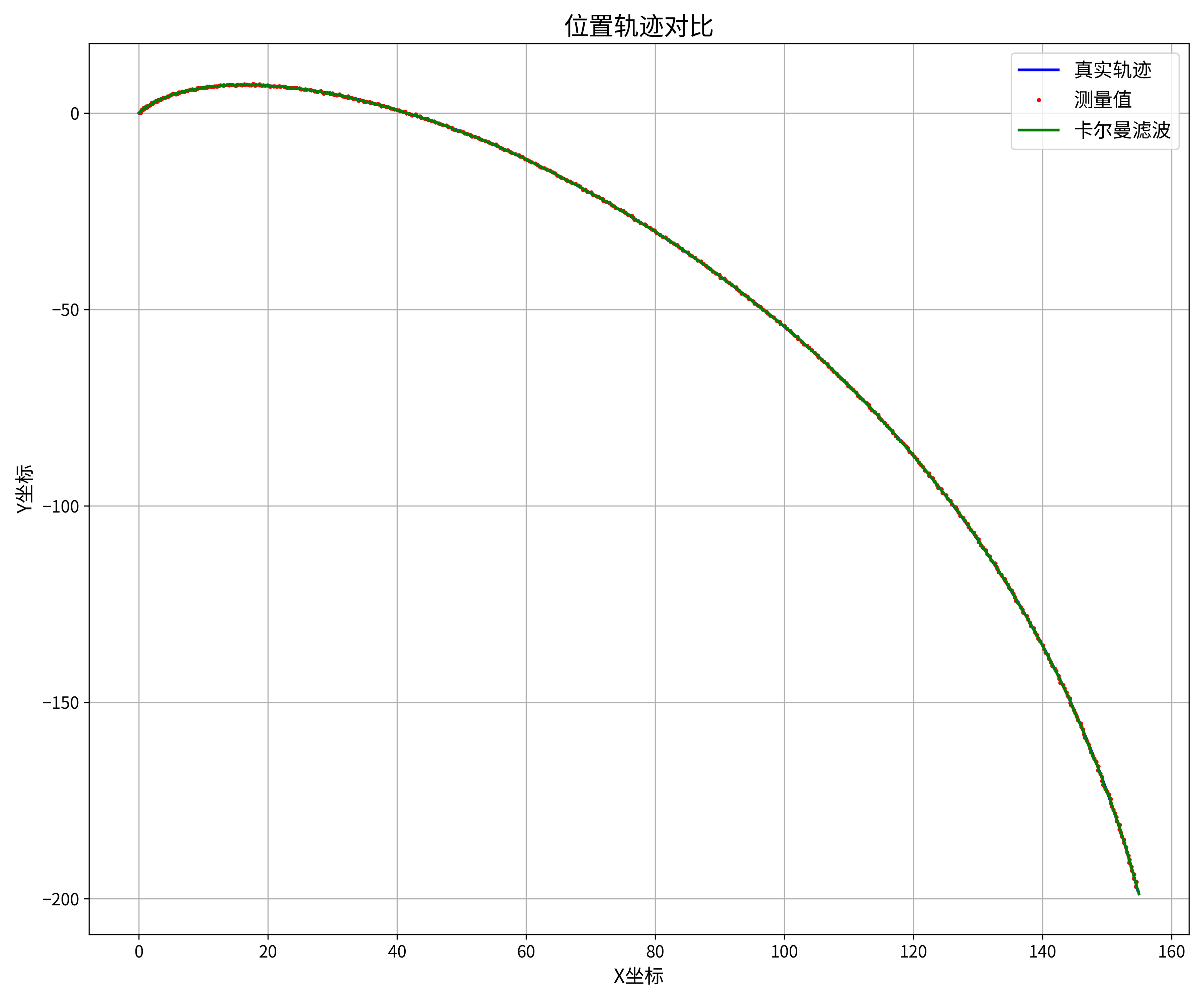
# 图1:位置轨迹对比
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 10))
plt.plot(df['真实位置X'], df['真实位置Y'], 'b-', linewidth=2, label='真实轨迹')
plt.plot(df['测量位置X'], df['测量位置Y'], 'r.', markersize=4, label='测量值')
plt.plot(df['估计位置X'], df['估计位置Y'], 'g-', linewidth=2, label='卡尔曼滤波')
plt.grid(True)
plt.legend(fontsize=14)
plt.title('位置轨迹对比', fontsize=18)
plt.xlabel('X坐标', fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel('Y坐标', fontsize=14)
plt.tick_params(axis='both', which='major', labelsize=12)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig(os.path.join(save_dir, '1_位置轨迹对比.png'), dpi=300)
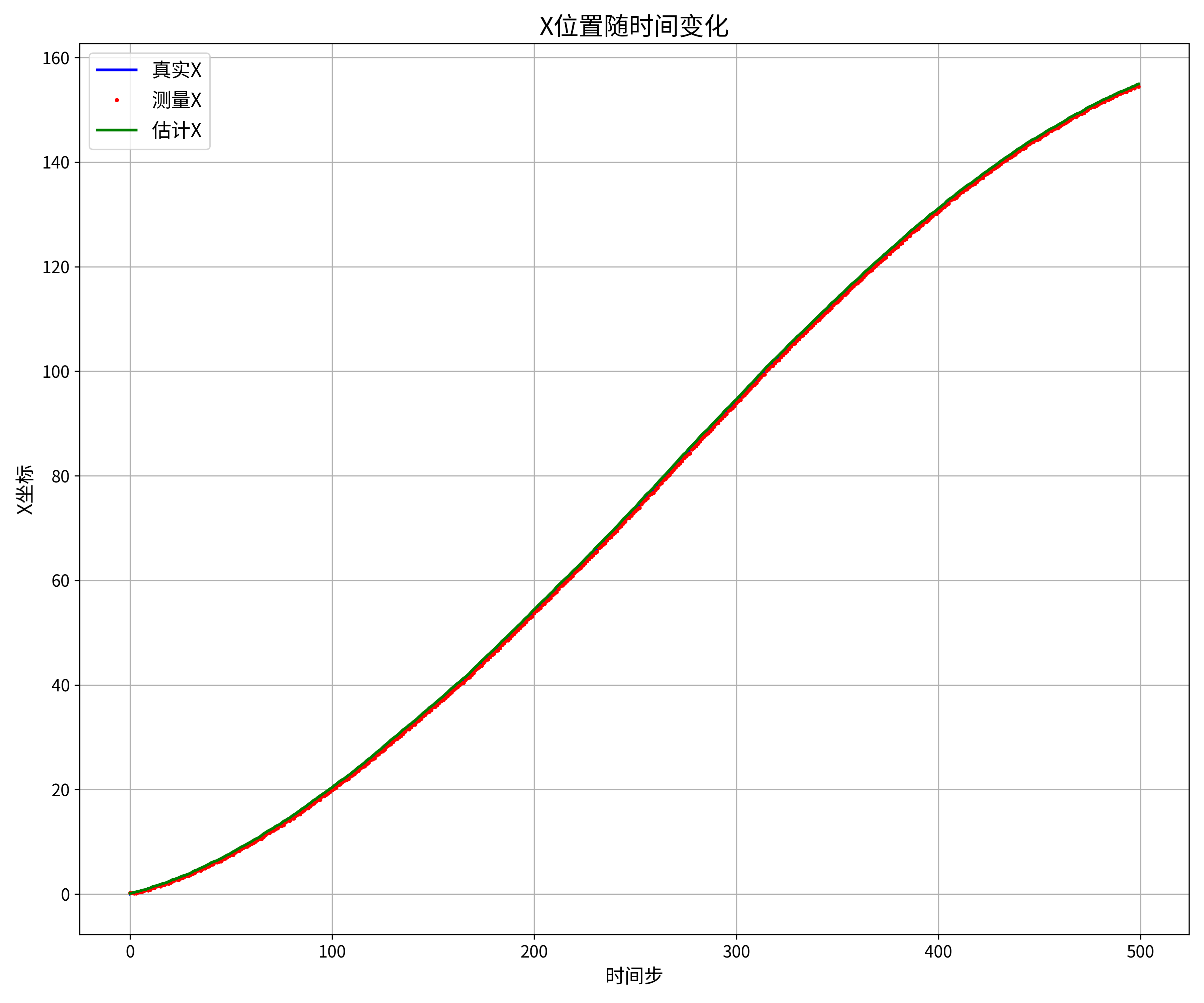
# 图2:X位置随时间变化
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 10))
plt.plot(df['时间步'], df['真实位置X'], 'b-', linewidth=2, label='真实X')
plt.plot(df['时间步'], df['测量位置X'], 'r.', markersize=4, label='测量X')
plt.plot(df['时间步'], df['估计位置X'], 'g-', linewidth=2, label='估计X')
plt.grid(True)
plt.legend(fontsize=14)
plt.title('X位置随时间变化', fontsize=18)
plt.xlabel('时间步', fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel('X坐标', fontsize=14)
plt.tick_params(axis='both', which='major', labelsize=12)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig(os.path.join(save_dir, '2_X位置随时间变化.png'), dpi=300)
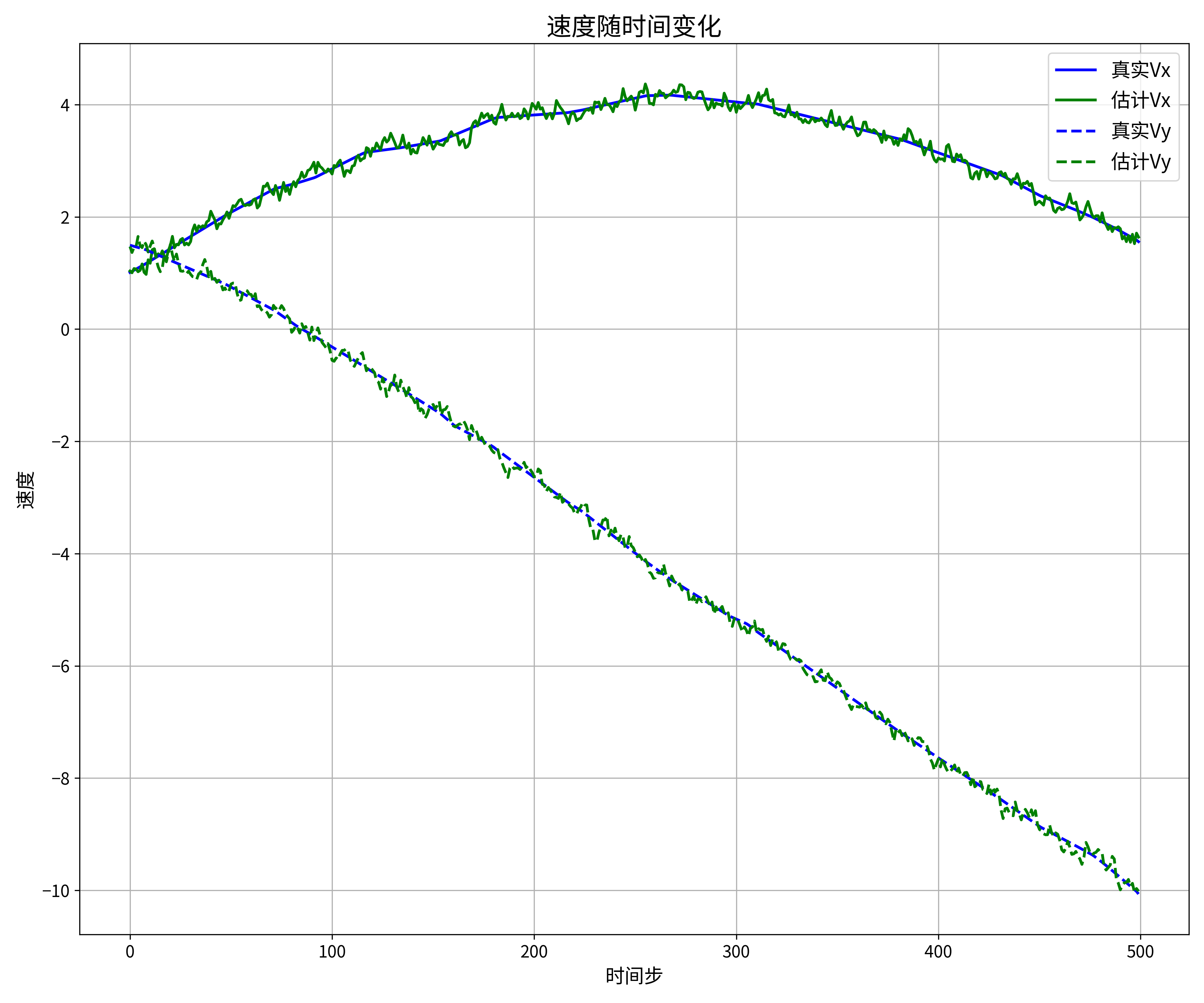
# 图3:速度随时间变化
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 10))
plt.plot(df['时间步'], df['真实速度X'], 'b-', linewidth=2, label='真实Vx')
plt.plot(df['时间步'], df['估计速度X'], 'g-', linewidth=2, label='估计Vx')
plt.plot(df['时间步'], df['真实速度Y'], 'b--', linewidth=2, label='真实Vy')
plt.plot(df['时间步'], df['估计速度Y'], 'g--', linewidth=2, label='估计Vy')
plt.grid(True)
plt.legend(fontsize=14)
plt.title('速度随时间变化', fontsize=18)
plt.xlabel('时间步', fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel('速度', fontsize=14)
plt.tick_params(axis='both', which='major', labelsize=12)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig(os.path.join(save_dir, '3_速度随时间变化.png'), dpi=300)
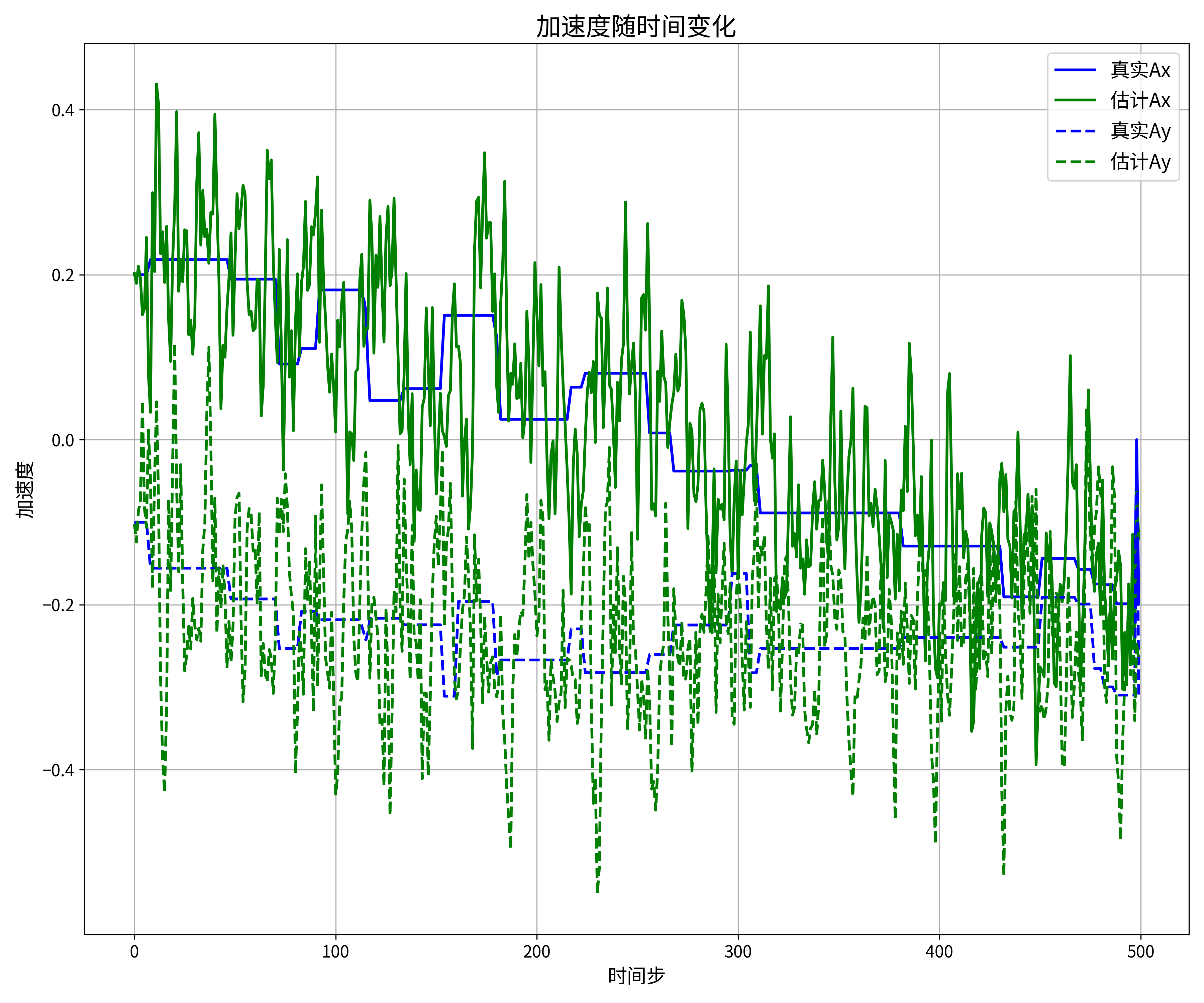
# 图4:加速度随时间变化
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 10))
plt.plot(df['时间步'], df['真实加速度X'], 'b-', linewidth=2, label='真实Ax')
plt.plot(df['时间步'], df['估计加速度X'], 'g-', linewidth=2, label='估计Ax')
plt.plot(df['时间步'], df['真实加速度Y'], 'b--', linewidth=2, label='真实Ay')
plt.plot(df['时间步'], df['估计加速度Y'], 'g--', linewidth=2, label='估计Ay')
plt.grid(True)
plt.legend(fontsize=14)
plt.title('加速度随时间变化', fontsize=18)
plt.xlabel('时间步', fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel('加速度', fontsize=14)
plt.tick_params(axis='both', which='major', labelsize=12)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig(os.path.join(save_dir, '4_加速度随时间变化.png'), dpi=300)
# 显示所有图形
plt.show()最终效果如下